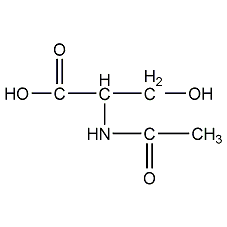
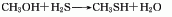Structural formula
| Business number | 017M |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 89.09 |
| label |
L-alpha-alanine, L-(+)-alanine, L-Oil amino acid, L-2-aminopropionic acid, 3-aminopropionic acid, (S)-2-Aminopropionic acid, L-α-Aminopropionic acid, L-a-Alanine, Enzymes and flavor enhancers |
Numbering system
CAS number:56-41-7
MDL number:MFCD00064410
EINECS number:200-273-8
RTECS number:AY2990000
BRN number:1720248
PubChem number:24891260
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless orthorhombic crystals or crystalline powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.432
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 297
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º, C=10, in water ): +2.42
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol , insoluble in ether and acetone.
Toxicological data
1. Mutagenicity: sister chromatids exchangeTEST system: human lymphocytes: 50mg/L
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 21.00
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol) 76.7
p>
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 199.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 45.8
5. Polarizability (10 -24cm3): 8.32
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 63.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 61.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 1
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
Store in a sealed, cool and dry place.
Synthesis method
1. The propionic acid chlorination and ammoniation method uses propionic acid as raw material. In the presence of 105°C temperature and 3% red phosphorus catalyst, liquid chlorine is introduced for chlorination to generate 2-chloropropionic acid, and then enters ammonia In an aqueous solution, using methenamine as a catalyst, ammoniation is carried out at a temperature of 60°C to generate 2-aminopropionic acid. Finally, the reactant is sent into a methanol solution for crystallization, centrifuged, and dried to obtain α-alanine finished product. 2. α-Bromopropionic acid chlorination method: Mix α-bromopropionic acid, ammonia and ammonium bicarbonate and reflux for 7 hours, then evaporate to dryness, then soak in ethanol to wash away the ammonium bromide, filter out the crystals, and then filter through decolorization , add ethanol to obtain crystallization, filter and dry to obtain the finished product. 3. Cyanohydrin method: Acetaldehyde reacts with hydrocyanic acid to generate cyanohydrin, which is then reacted with ammonia to obtain aminonitrile; then it is hydrolyzed under alkaline conditions to generate sodium aminopropionate, and L-alanine is obtained through ion exchange.

2. Mainly uses L-aspartic acid as raw material, which is obtained bydecarboxylation, enzyme killing, decolorization, filtration, crystallization, centrifugation, washing and drying. Finished product.

3.Enzymatic method

4.Immobilized enzyme

5.Acrylonitrile method acrylonitrile React with ammonia in a solution of diphenylamine and tert-butyl alcohol at 109°C and 1176.798KPa pressure to generate β-aminopropionitrile:

Then it reacts with sodium hydroxide to generate β- Sodium aminopropionate:
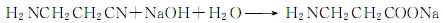
Finally acidify with hydrochloric acid to generate β-aminopropionic acid:
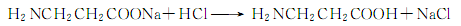
6.β-aminopropionitrile method consists of β-aminopropionitrile Obtained by hydrolysis and acid precipitation.

7. Tobacco: BU, 21; FC, 20. In the experiment, acid hydrolysis of silk fiber (degummed white silk) was used.
8. Obtain orthorhombic crystals from water.
Purpose
1. Biochemical research. Tissue culture. Liver function tests.
2.Used as a flavor enhancer. It can increase the seasoning effect of condiments; it can also be used as a sour taste corrector to improve the sour taste of organic acids.
3.β-Alanine is used as Additive substances for electroless plating and electroplating, and also used in the preparation of electroplating corrosion inhibitors.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/694extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-6425-39-4/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45111extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-9726/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/potassium-neodecanoate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-t-catalyst-cas10294-43-5-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dabco-ncm-polyester-sponge-catalyst-dabco-ncm/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/75.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Polyurethane-Catalyst-SA102-NTCAT-SA102-SA102.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1604