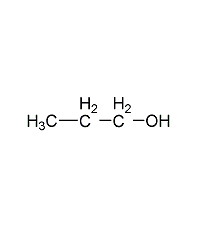
Structural formula
| Business number | 01GD |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H8O |
| Molecular weight | 60.10 |
| label |
n-Propanol, n-Propanol, n-Propyl alcohol, Optal, AlcoholC3, Propylic alcohol, thinner, dental detergent, pesticides, fungicides, antifreeze, adhesive, paint solvents, alcohol compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:71-23-8
MDL number:MFCD00002941
EINECS number:200-746-9
RTECS number:UH8225000
BRN number:1098242
PubChem number:24856894
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with mellow smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -127[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 97.1[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.80[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.1[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.0 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2021.3[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 263.6[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.17[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.25 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 15[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 371 [12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 13.5[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%) : 2.1[14]
15. Solubility: Miscible with water, miscible with most organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 2.26
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, b.p.): 680.8
18. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 5.20
19. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): -300.9
20. Specific heat capacity (KJ/( kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 2.45
21. Boiling point rising constant: 1.59
22. Conductivity (S/m, 18ºC): 9.17×10-9
23. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 20ºC): 1.7166
24. Volume expansion coefficient (K– 1, 20ºC): 0.00107
25. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.7998
26. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.3837
27. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.276
28. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 218
29. Critical compression factor: 0.252
30. Eccentricity factor: 0.628
31. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 8.361
32. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 223.0
33. Solubility parameter (J·cm– 3)0.5: 24.557
34. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1 ): 6.280×109
35. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 42.170
36. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1): 2068.65
37. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -255.18
38. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 322.58
39. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ ·mol-1): -159.8
40. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 85.56
41. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2021.12
42. Liquid phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -302.71
43. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1· K-1): 192.80
44. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -168.78
45. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 143.8
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 1870mg/kg (rat oral); 6800mg/kg (mouse Oral); 2825mg/kg (rabbit oral); 5040mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 48000mg/m3 (mouse inhalation)
2. Irritation[17]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild irritation (open irritation test).
Rabbit eye: 20mg (24h), moderate irritation.
3. Others[18] LDLo: Female 1870mg/kg
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[19]
LC50: 4.10~4.88g/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
IC50: 255~3100mg/L (72h) (algae)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[20] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 2.9d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 17.48
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 75.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 168.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 24.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 6.93
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 7.2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is miscible with various organic solvents such as water and alcohol, and can dissolve vegetable oils, animal oils, natural resins and some synthetic resins. Has an odor similar to ethanol. Non-corrosive to metals.
2. Chemical properties: Similar to ethanol, it is oxidized to produce propionaldehyde, which is further oxidized to produce propionic acid. Dehydration with sulfuric acid produces propylene.
3. It is of low toxicity. The physiological effects are similar to ethanol, but its anesthesia and mucous membrane irritation are slightly stronger than ethanol. It is also more toxic than ethanol and its bactericidal ability is three times stronger than ethanol. The olfactory threshold concentration is 73.62mg/m3. TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 200 mg/m3.
4. Stability[21] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[22] Strong oxidants, acid anhydrides, acids, halogens
6. Polymerization hazards[23] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, halogens, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Recovery method from isopropanol by-product: When propylene is directly hydrated to produce isopropanol, n-propanol is produced as a by-product, and n-propanol is produced from it.
![]()
2. Hydrogenation of propylene oxide Law.
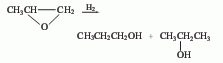
3. Propanaldehyde hydrogenation method : Propanol and allyl alcohol are produced by hydrogenating propionaldehyde and acrolein. 4. Allyl alcohol hydrogenation method. 5. Methanol method. 6. Ethylene oxo synthesis method. The third method is a commonly used method in industry. Catalysts include hydroxyl compounds of cobalt and rhodium, ruthenium complexes, skeleton catalysts (such as nickel, copper), etc. The most commonly used are skeleton catalysts. The production methods include gas phase hydrogenation and flat liquid phase hydrogenation. The pressure of gas-phase hydrogenation is about 0.7MPa, and copper-based catalysts are mostly used; the pressure of liquid-phase hydrogenation is 2~4MPa, and nickel-based catalysts are mostly used.

4. Propionaldehyde is obtained through oxo synthesis of ethylene, and then n-propanol is obtained after hydrogenation. Alternatively, metal carbonyl compounds are used as catalysts to synthesize ethylene from ethylene. It can also be produced directly with water through liquid-phase oxidation of propane or butane.
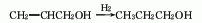
5. The reaction formula of the methanol method is as follows:
![]()
6. The reaction formula of vinyl carbonylation method is as follows:
![]()
7. Use industrial n-propanol as raw material, first add bromine (1.5ml of bromine water per liter of n-propanol), After mixing evenly, crudely evaporate once, add a small amount of potassium carbonate to the crude product for distillation, take the middle fraction, add a desiccant for dehydration, and finally distill the middle fraction, which is the pure product.
Purpose
1. Propanol is used directly as a solvent or to synthesize propyl acetate. It is used in coating solvents, printing inks, cosmetics, etc. It is used in the production of n-propylamine, an intermediate for medicines and pesticides, and in the production of feed additives, synthetic flavors, etc. Propanol is used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce probenecid, sodium valproate, erythromycin, epileptic acid, adhesive hemostatic agent BCA, propylthiamine, dipropyl 2,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, etc.; Various esters synthesized from propanol are used in many aspects such as food additives, plasticizers, spices, etc. Derivatives of n-propanol, especially di-n-propylamine, have many applications in medicine and pesticide production, and are used to produce pesticide aminesulfonate. Lingmao, Diprofen, Propyrrolidone, Sulfuroxime, Trifluralin, etc.
2. Used as a solvent for vegetable oils, natural rubber and resins, some synthetic resins, ethyl cellulose, and polyvinyl butyral. It is also used in nitrocellulose spray paint, coatings, cosmetics, dental detergents, insecticides, fungicides, inks, plastics, antifreeze, adhesives, etc.
3. Generally used as solvent. It can be used as coating solvents, printing inks, cosmetics, etc., as an intermediate in the production of medicines and pesticides, and as an intermediate in the production of feed additives, synthetic flavors, etc. Propanol is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry, food additives, plasticizers, spices and many other aspects.
4. Used as solvent and used in pharmaceuticals, paints and cosmetics, etc. [25]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44242extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1734extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-23850-94-4-2/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/43960extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44543extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44151extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/115-4.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-c-225/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/low-odor-reaction-type-9727-catalyst-9727-reaction-type-catalyst-9727/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40470</b