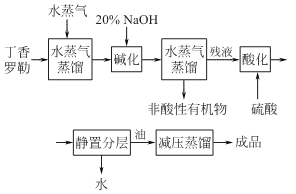
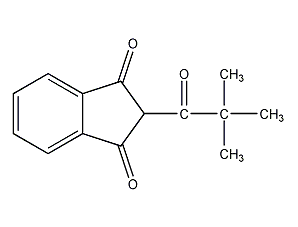
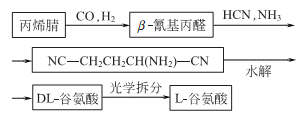
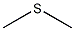Structural formula
| Business number | 01J6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CaC2 |
| Molecular weight | 64.10 |
| label |
Carbide Level 4, calcium carbide, Calcium acetylide, Acetylenogen, other |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-20-7
MDL number:MFCD00010905
EINECS number:200-848-3
RTECS number:None
BRN number:3909011
PubChem number:24856368
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: Colorless crystals, industrial products are gray-black lumps, and the cross-section is purple or gray. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 2300[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): decomposition [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 2.22[4]
5. Octanol/ Water distribution coefficient: -0.30[5]
6. Ignition temperature (℃): >325[6]
7.Solubility: No data yet
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity No data available
2. Irritation No data available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[7] This substance is harmful to the environment and should be specially Pay attention to water pollution.
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 8
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 61.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 18
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 271
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[8] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[9] Water, alcohols, acids
3. Conditions to avoid contact[10] Humid air
4. Hazards of aggregation[11] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[12] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated special warehouse with a temperature not exceeding 32°C and a relative humidity not exceeding 75%. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and protected from moisture. It should be stored separately from acids, alcohols, etc. and avoid mixed storage. The storage area should be equipped with appropriate� materials to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. The electric furnace reduction method is currently the only method for industrial production of calcium carbide. This method was industrialized in the United States as early as 1895. The production involves high-temperature operations, a lot of dust, and high power consumption. Improvements in the process can improve operating conditions, reduce heat loss, and increase carbon monoxide recovery and utilization. Closed and large-scale Calcium carbide furnace. Crush the coke and lime, mix them evenly according to the proportion, add them to a closed calcium carbide furnace, heat them with electricity, and perform a reduction reaction at 2000-2200°C to generate molten calcium carbide, which flows from the furnace into a calcium carbide pot for cooling, crushing, and packaging. kg/ton of coke (84% fixed carbon) 550 limestone (CaO92%) 840 electrode paste 30 electricity 3200 (degree/ton)
2. Calcium carbide can be directly produced from the two elements of carbon and metallic calcium in an electric arc furnace Synthetically, or by reacting calcium oxide and carbon in an electric arc furnace at a high temperature of 2000°C. The purity of the products produced by these two methods is not high. The purity of calcium carbide produced by heating calcium cyanamide CaCN2 or calcium cyanamide and carbon in high vacuum can reach 99%.
The alumina boat is filled with pure calcium cyanamide or a mixture of calcium cyanamide and acetylene carbon black (or sugar charcoal), and the boat is placed in a ground-mouthed high-aluminum vessel with one end closed. To make porcelain tubes, this tube is connected to a vacuum pump and heated with a molybdenum wire furnace.
Heating CaCN2 or the mixture of CaCN2 and C must be carried out in two steps: the first step is to heat to 1100~1150℃ for 2~3 hours in high vacuum to fully decompose CaCN2 and remove as much N2 as possible. At this time, care should be taken to control the temperature not to exceed 1150°C to avoid the formation of a CaCN2CaC2 eutectic at 1170°C. In the second step, continue to raise the temperature to 1350°C for 1 hour, remove the remaining N2, and obtain pure white calcium carbide. Purity reaches 99%.
Attached is the preparation method of calcium cyanamide. Pure HCN is dried by CaCl2 and P2O5 and condensed in a low-temperature receiver. The collection amount should be equal to 3 times the calculated amount. Put CaCO3 in a porcelain boat, place the porcelain boat in a porcelain tube, and heat the porcelain tube to 700~850°C. Then warm the HCN receiver to 18°C. N2 gas mixed with a small amount of NH3 is used to carry HCN through CaCO3, and pure white CaCN2 can be obtained after 3 hours, with a purity of 99.4%.
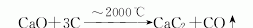
Purpose
1. About 60% of calcium carbide is used in chemical production, and the remaining 40% is used in metal welding and cutting. A series of chemical products can be produced using calcium carbide as raw materials, such as PVC resin, polyvinyl alcohol, vinyl acetate, chloroprene rubber, butanol, octanol, tricyanethylene, tetracyanoethylene, acetaldehyde, acetylene carbon black, lime nitrogen, etc. . The largest consumption is the production of PVC resin, accounting for 60% of the consumption of calcium carbide for chemical industry. Calcium carbide powder is irritating and can damage the skin and respiratory system.
2. It is an important basic chemical raw material, mainly used to produce acetylene gas and calcium cyanamide. Also used in organic synthesis, etc. [13]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Jeffcat-ZF-22-MSDS.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1081extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40267extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45149extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Tegoamin-BDE.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-tka30-catalyst-nitro/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/polyurethane-monosodium-glutamate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/tmr-4-dabco-tmr-4-trimer-catalyst-tmr-4/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Dioctyl-dimaleate-di-n-octyl-tin-CAS33568-99-9-Dioctyl-dimaleate-di-n-octyl-tin.pdfextended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/category/product/page/33/