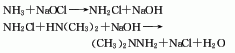
Structural formula
| Business number | 01JF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7I |
| Molecular weight | 169.99 |
| label |
isopropyl iodide, 2-iodopropane, Iodoisopropane, Isopropyl iodide, 2-Propyl iodide, (CH3)2CHI, Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-30-9
MDL number:MFCD00001071
EINECS number:200-859-3
RTECS number:TZ4200000
BRN number:1098244
PubChem number:24881578
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 1.7042
3. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.6946
4. Melting point (ºC): -90.1
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 89.5
6. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -74.0
7. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4991
8. Flash point (ºC): 42
9. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4961
10. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5 sup>:17.784
11. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.290×109
12. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 53.300
13. Liquid phase standard Hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 137.0
14. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -40.3
15. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 324.58
16. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 21.5
17. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 90.08
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19 . Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible with ethanol, ether and benzene.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Rat inhalation LC50: 320gm/m3/30M
Mouse abdominal LD50: 1300mg/kg
2. Chronic toxicity /Carcinogenicity:
Mouse abdominal LD50: 1190 mg/kg/8W-I
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 28.87
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 97.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 222.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 27.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.44
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 10.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Colorless liquid, changes color when exposed to air and light. It decomposes when exposed to high heat or burned and releases toxic gases. Highly flammable and can burn when exposed to open flames.
Storage method
This product should be stored in a sealed, cool, dry place.
Synthesis method
1. It is produced by reacting isopropyl alcohol with iodine and red phosphorus; it can also be produced by distilling glycerin and hydrogen iodide or by heating and refluxing isopropyl chloride and potassium iodide acetone solution together.
2. Preparation method:
![]()
In a round-bottomed flask equipped with a distillation device, add 30g (0.5mol) isopropyl alcohol (2) and 450g (265mL) azeotropic hydriodic acid. Heating and distilling in an oil bath, controlling the evaporation rate to 1 to 2 drops per second. Stop distilling when about half of the liquid has evaporated. The lower oil in the distillate was separated to obtain 70g of crude 2-iodopropane (1). Wash with an equal volume of concentrated hydrochloric acid, then wash with water, 5% sodium carbonate, and water in sequence, dry with anhydrous calcium chloride, and distill. Collect the fractions at 87 to 89°C to obtain 2-iodopropane. [1]
Purpose
Solvents, organic synthesis intermediates.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1686extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/low-atomization-catalyst-9727/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-mb20-bismuth-metal-carboxylate-catalyst-catalyst-dabco-mb20/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44233extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/elastomer-environmental-protection-catalyst-nt-cat-e-129/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/102-6.jpgextended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/non-emission-delayed-amine-catalyst-dabco-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat2001-catalyst-cas301-10-0-stannous-octoate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/bismuth-neodecanoate-cas34364-26-6-bismuth-neodecanoate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/low-atomization-amine-catalyst/