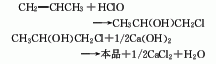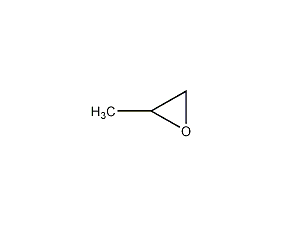
Structural formula
| Business number |
01JR |
| Molecular formula |
C3H6O |
| Molecular weight |
58.08 |
| label |
propylene oxide,
Epoxy propylene,
Propylene oxide,
propylene oxide,
Methyl ethylene oxide,
Propylene Oxide,
Aliphatic alcohols, ethers and their derivatives
|
Numbering system
CAS number:75-56-9
MDL number:MFCD00005126
EINECS number:200-879-2
RTECS number:TZ2975000
BRN number:79763
PubChem number:24880314
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -112[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 34[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.83[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.0[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 71.7 (25℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1755.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 209.1[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.93[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.03 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -37 (CC); -28.8 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 449[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 36.0[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.3[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, miscible in methanol, ether, acetone, benzene, tetracycline Most organic solvents such as carbon chloride. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 0ºC): 0.410
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.327
18. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 6.5
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 15ºC, constant pressure): 1.95
20 .Body expansion coefficient (K-1, liquid): 0.00213
21. Combustion range in air (ml/100ml): 2.1~2.15
22 .Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.305
23. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 190
24. Critical compression factor: 0.245
25. Eccentricity factor: 0.271
26. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 4.8515
27. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 239.00
28. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 19.110
29. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 4.640×109
30. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 34.400
31. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1943.34
32. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1) : -94.68
33. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 281.15
34 .Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -25.1
35. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1· K-1): 72.55
36. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1915.44
37. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy)( kJ·mol-1): -122.59
38. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K– 1): 196.27
39. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -28.66
40. Liquid Phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 122.5
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 380mg/kg (rat oral); 1245mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 4000ppm (rat inhalation, 4h); 4127mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[17]
Rabbit transdermal: 50mg (6min), severe irritation; 415mg , moderate stimulation (open stimulation test).
Rabbit eye: 20mg (2h), moderate irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[18] 0.3g/kg by gavage, 5 times a week, 18 times, the rats lost weight, suffered gastric irritation and liver damage.
4. Mutagenicity[19] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 350μg/dish. DNA damage: E. coli 1μmol/L. Dominant lethal experiment: rats inhaled 300ppm (5d) (intermittent). Cytogenetic analysis: human lymphocytes 1850 μg/L. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 25,000 ppm.
5. Teratogenicity[20] The lowest toxic dose of inhalation (TCLo) in rats 7~16 days after pregnancy 500ppm (7h), causing developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system and craniofacial area (including nose and tongue).
6. Carcinogenicity[21] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2B, suspected human carcinogen.
7. Others[22] The lowest inhalation toxic concentration in rats (TCLo): 500ppm (7h) (pregnant 7 to 16 days after administration), it can cause embryotoxicity and abnormal musculoskeletal development.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[23]
LC50: 170mg/L (24h) (goldfish)
TLm: 141mg/L (96h) (mosquito fish, static);
215mg/L (96h) (bluegill sunfish, static)
2. Biodegradability[24] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 96% degradation after 2 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[25]
In the air, when hydroxyl groups are free When the base concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 30 days (theoretical).
At 25℃, when the pH value is 7~9.5, the hydrolysis half-life is 11.6d and 6.6d respectively (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 15.53
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 64.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 144.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 6.15
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 26.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Low boiling flammable liquid with ether smell. The industrial product is a racemic mixture of two optical isomers. Propylene oxide is a flammable and explosive chemical and its vapors will decompose. Excessive amounts of acidic salts (such as tin chloride, zinc chloride), alkalis, and tertiary amines that may contaminate propylene oxide should be avoided. Non-corrosive to metals. Due to its effect on certain rubbers and plastics, care should be taken when selecting gaskets and valves. Due to its low boiling point, high volatility, flammability, and active chemical properties, care should be taken to prevent it from being close to sparks, static electricity, heat sources, acids, alkali, etc. Partially miscible with water [solubility in water at 20°C is 40.5% (weight); solubility of water in propylene oxide is 12.8% (weight)], miscible with ethanol and ether, and with methylene chloride, pentane, and pentene , cyclopentane, cyclopentene, etc. form a binary azeotrope.
2. It has extremely active chemical properties, especially it can react with compounds containing active hydrogen to generate various derivatives. For example, it reacts with water to form 1,2-propanediol; reacts with ammonia to form isopropanolamine; reacts with alcohol to form hydroxy ether; reacts with fatty acid to form hydroxy ester; reacts with hydrogen halide to form halohydrin; reacts with propylene glycol to form polypropylene glycol ; Oxidation generates acetic acid; reacts with glycerin to generate polyether triol; reacts with carboxylic acid to generate ester, etc. When it passes through pumice at 500°C, it is partially rearranged to produce acetone and propionaldehyde. It reacts with chlorine in anhydrous state to generate chloroacetone and 1-chloro-2-propanol. Acetic acid is produced during oxidation, and isopropanol is produced by reduction with sodium amalgam.
3. Stability[26] Stable
4. Incompatible materials[27] Acids, alkalis, strong oxidants. Anhydrous chlorides of iron, tin and aluminum, peroxides of iron and aluminum, ammonia, chlorosulfonic acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrogen fluoride, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, fuming sulfuric acid, etc.
5. Avoid Contact conditions[28] Heating
6. Polymerization hazard[29] No polymerization p>
Storage method
1. Storage precautions [30] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. Propylene oxide is a low-boiling, flammable liquid. Its vapor can spontaneously ignite or explode in the air. It should be stored and transported according to the regulations on toxic and dangerous goods. Storage tanks and reactors should be covered with inert gas. The temperature and pressure of the container should be kept below 25°C and 0.3Mpa. Implement relevant fire and explosion safety measures. Storage and transportation containers should be made of stainless steel.
Synthesis method
1. Chlorohydrin method: Propylene, chlorine, and water are hypochlorous at normal pressure and 60°C to generate chloropropanol, which is then saponified, condensed, and distilled. Process flow: (1) Propylene hypochlorination: Pass propylene and chlorine into water respectively for gas-liquid phase reaction. The reaction temperature is 35-50°C, and the molar ratio of propylene to chlorine is (1.1-1.2): 1. Water and chlorine first react to form hypochlorous acid, and then propylene reacts with hypochlorous acid to form chloropropanol. In order to reduce side reactions and avoid the generation of dichloropropane, the concentration of chloropropanol should not be too high, generally not higher than 6%-7%; chlorine should not be excessive. In addition to excessive chlorine causing an increase in the by-product dichloroethane, it also There is a risk of explosion; when passing chlorine and propylene into the reactor, direct contact between the two gases should be avoided as much as possible. Generally, the chlorine gas inlet is located below the propylene inlet, and the water inlet is located at the bottom.
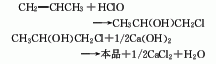
(2) Chloropropanol removal Hydrogen chloride reaction: Add water-containing chloropropanol into the saponification kettle, then add 10% lime milk, and stir to perform the saponification reaction. During the process, attention must be paid to the adding method of materials. If chloropropanol is added to lime milk, the resulting When propylene oxide is in an alkaline medium, it will hydrolyze to form propylene glycol. Therefore, for the dehydrochlorination of chloropropanol, alkali must be added to the chloropropanol to obtain the highest possible yield of propylene oxide. The propylene oxide formation reaction is immediately evaporated to avoid hydrolysis. (3) Purification of propylene oxide: After condensation, the steamed propylene oxide is sent to the distillation tower for distillation to obtain the finished product.
2. Direct oxidation method: It is produced by oxidizing propylene with oxygen or air under the action of silver catalysis.
3. Indirect oxidation method: ethylbenzene (or isobutane, cumene, etc.) is oxidized to produce ethylbenzene hydroperoxide (or tert-butyl hydroperoxide, cumene hydroperoxide) Benzene, etc.), obtained by epoxidation reaction with propylene in the presence of catalysts such as molybdenum naphthenate.
4. Electrochemical chlorohydrin method: This method uses the principle of electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (or potassium chloride, sodium bromide, sodium iodide) to generate chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide. Propylene is introduced into the zone to generate chloropropanol. In the cathode zone, chloropropanol reacts with sodium hydroxide to generate propylene oxide.
5. Peroxide method: The main process is the production of organic hydrogen peroxide, and propylene is oxidized with peroxide. Whether the reaction is producing organic hydrogen peroxide or transferring the oxygen of the peroxide to propylene molecules in the presence of a catalyst, it is a liquid phase reaction. In addition to the main product propylene oxide, this method also has co-products. At present, the Haakon process of ethylbenzene and Haakon process of isobutane have been industrialized.
(1) Ethylbenzene Haakon method: ethylbenzene is used as raw material and oxidized to produce ethylbenzene hydroperoxide. Under the action of catalysts such as copper naphthenate, the propylene epoxidation reaction is performed to obtain propylene oxide. At the same time, α-phenylethyl alcohol is obtained, and styrene can be obtained after dehydration.
The reaction temperature of ethylbenzene oxidation is 130~150℃, the pressure is 0.07~0.14 MPa, the selectivity of generating ethylbenzene hydroperoxide is 90%, the epoxidation temperature is 50~120℃, the pressure is normal Pressure 0.1 ~ 0.864 MPa. For example, add 0.4% manganese naphthenate-sodium naphthenate (nMo /nNa=2, molar ratio) as the catalyst, reacted at 100°C for 1.5 h, and obtained the conversion rate of ethylbenzene hydroperoxide 99%, and the option of generating propylene oxide The property is 78%. The reaction product can be distilled to obtain the finished product propylene oxide, while α-phenylethyl alcohol is treated with TiO3-Al2O3As a catalyst, it is dehydrated at 250~280℃ and converted into styrene 100%, with a selectivity of 92%. The characteristics of this method are: low cost, economical and reasonable, less three wastes, and co-production of styrene.
(2) Isobutane Haakon process: It uses isobutane as raw material, reacts with propylene through the oxidant tert-butyl hydroperoxide to obtain propylene oxide and tert-butanol. The process is similar to the ethylbenzene Haakon process. similar. The preparation of tert-butyl hydroperoxide is at 100~110℃ without a catalyst. Usually tert-butyl hydroperoxide is used as a secondary initiator, and the reaction of propylene epoxidation isThe conditions are reaction temperature 121°C and pressure 4.1 MPa. It was carried out in the presence of molybdenum catalyst, the reaction time was 0.5 h, the yield of propylene oxide was 88% (calculated as peroxide), and the selectivity was 81%. This method can co-produce tert-butyl alcohol with a yield of about 60%.
Purpose
1. Propylene oxide is an important organic chemical raw material and the third largest product of the propylene series. Its largest use is to make polyether polyols and then polyurethane. In the distribution of uses in the United States and Western Europe, this use Accounting for more than 60% and 70% respectively. Used in the manufacture of nonionic surfactants and propylene alcohol, propylene glycol, alcohol ethers, propylene carbonate, isopropanolamine, propionaldehyde, synthetic glycerin, organic acids, synthetic resins, foam plastics, plasticizers, emulsifiers, and wetting agents , detergents, bactericides, fumigants, etc. Fine chemicals derived from propylene oxide are used in almost all industrial sectors and in daily life. In addition, propylene oxide is also used in small amounts in coatings, brake fluids, antifreeze, jet engine fuel additives, floor polishes, printing inks, electronic chemicals, cleaners, mineral processing agents, leather processing, photosensitive fluids for PS plates, short-acting Plasticizers, dyes, non-ionic surfactants, oil field demulsifiers, flame retardants, pesticide emulsifiers and wetting agents and other industries. Also used in organic synthesis. It is used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, and various resins, a stabilizer for vinyl chloride resin and chlorine-containing solvents, and a fading inhibitor for nitrocellulose spray paint. It is also used in the manufacture of surfactants (wetting agents, detergents, emulsifiers, etc.) as well as medicines, pesticides, spices, and artificial leather.
2. Used to prepare modified epoxy resin curing agent, synthetic resin and reactive diluent as epoxy resin adhesive. It is also used in the production of propylene glycol, propylene alcohol, propionaldehyde, polyether, isopropanolamine, higher fatty acid ester surfactants, plasticizers, medicines, pesticides, spices, and foam products. It is also a solvent for various resins, cellulose acetate, nitrocellulose, etc., a stabilizer for vinyl chloride resin and chlorine-containing solvents, a fading preventer for nitro spray paint, and can also be used as a bactericide, fumigant, wetting agent, etc. It is a broad-spectrum disinfectant that can kill bacterial propagules, spores, fungi and viruses. The general sterilization concentration is 800~2000mg/L.
3. It is an important raw material for organic synthesis. It is used to synthesize lubricants, surfactants, detergents, manufacture pesticides, and produce polyurethane foams and resins. [31]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-2273-43-0-2/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-c-323-tertiary-amine-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/polycat-sa102-niax-a-577/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/high-rebound-delayed-catalyst-c-225/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1763extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/n-3-dimethyl-amino-propyl-n-n-diisopropanolamine/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/43979extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/526extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-td-25-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44968