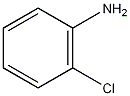
Structural formula
| Physical competition number | 0298 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6ClN |
| Molecular weight | 127 |
| label |
o-Chloroaniline, o-Aminochlorobenzene, 2-Chloroaniline, 2-Chlorobenzenamine, o-Aminochlorobenzene, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:95-51-2
MDL number:MFCD00007656
EINECS number:202-426-4
RTECS number:BX0525000
BRN number:606077
PubChem number:24853944
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless, transparent to light yellow oily liquid with ammonia odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -1.94[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 209[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.21[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.4[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (46.3℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.59[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.9[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 97; 103 (CC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 500 [10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.8[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%) : 1.5[12]
13. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and most organic solvents. [13]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse oral LD50: 256g/kg; cat skin contact LD50: 222mg/kg; cat subcutaneous LDLo: 310mg/kg;
2. Other multiple dose toxicity : Inhalation TDLo in rats: 14560mg/kg/13W-I; Oral TDLo in mice: 14560mg/kg/13W-I;
3. It is moderately toxic. Easily absorbed by the skin and has hemolytic effect. Can damage the liver and kidneys and cause bladder cancer. The symptoms of poisoning are similar to those of aniline.
4. Acute toxicity[14] LD50: 256mg/kg (mouse oral)
5. Irritation No information available
6. Mutagenicity[15] DNA repair: E. coli 500μg/L. Microbial mutagenicity: Aspergillus nidulans 200mg/L. Mammalian somatic mutation: hamster lung 600μg/L.
Ecological data
1. This substance is harmful to the environment. It is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
2. Ecotoxicity[16]
LC50: 5.65mg/L (96h ) (fathead minnow, dynamic); 6.3mg/L (48h) (medaka)
EC50: 4.2mg/L (24h), 1.8mg/L (48h) (water flea); 200mg /L (24h) (Tetrahymena pyriformis, static); 90mg/L (48h), 40mg/L (72h), 35mg/L (96h) (Scenedesmus, static)
3. Biodegradability[17] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, degradation 2.7% after 2 weeks.
4. Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 12h (theoretical).
5. Bioconcentration[19] BCF: 5.4~9 ( Carp, exposure concentration 0.1ppm, exposure time 8 weeks); <14~32 (carp, exposure concentration 0.01ppm, exposure time 8 weeks).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.38
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 103.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 268.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 45.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 14.02
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 74.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Due to the chlorine substitution on the aromatic nucleus, the basicity of o-chloroaniline (25℃, pKa=2.636) is much weaker than that of aniline (25℃, pKa=4.595). The chemical properties are similar to aniline and can form salts with inorganic acids, but the acylation reaction and diazotization reaction are slower.
2. This product is highly toxic. Poisoning may occur if swallowed, inhaled vapor or absorbed through skin. It is hemolytic and can cause bladder cancer. During operation, avoid inhaling vapor and prevent contact with skin. Production equipment should be sealed to prevent leakage. The production site should be well ventilated. Operators should wear protective equipment.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[21] Acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroform, strong oxidants
5. Conditions to avoid contact [22] Heating
6. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[24 ] Ammonia, chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
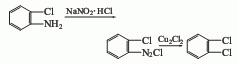
1. Obtained from the reduction of o-nitrochlorobenzene: reduce with iron powder in hydrochloric acid medium, reflux for 6-8 hours, and obtain the finished product through steam distillation and vacuum distillation. Iron powder reduction can also be carried out in the presence of formic acid: add 2m3 boiling water to a 10m3 cast iron reduction kettle, then add 100kg o-nitrochlorobenzene, 15kg formic acid, and 1.5t iron powder to perform the reduction reaction. Add 4t o-nitrochlorobenzene in portions within 17-20h. In the meantime, when the reduction reaction proceeds for a quarter of an hour, add 1t of o-nitrochlorobenzene, and at the same time, add 1.5t of iron powder and 15kg of formic acid. If the reaction is slow, add another 1t of iron powder. After the reaction is completed, let it stand to separate the amine layer, let it stand again, let the iron precipitate, and steam the iron slag to distill out the amine. The crude product was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 3160kg of o-chloroaniline with a yield of 95%. Raw material consumption quota: o-nitrochlorobenzene 1300kg/t, iron powder (90%) 1450kg/t, hydrochloric acid (37%) 380kg/t.
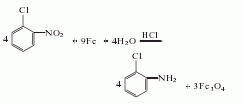
2. The preparation method is O-chloronitrobenzene, iron filings, dilute hydrochloric acid and water are refluxed for 6 to 8 hours, distilled to obtain a crude product, and then distilled to obtain a finished product.
Or use catalytic hydrogenation, that is, use o-chloronitrobenzene as raw material and hydrogenate it in the presence of a catalyst to obtain the finished product.
Refining method: o-chloroaniline is obtained by reducing o-chloronitrobenzene and then vacuum distillation. If it contains the para-isomer, it can be dissolved with an equal amount of sulfuric acid and then steam distilled. The para-isomer remains in the form of sulfate for separation purposes. It can also be dissolved in 10% hot hydrochloric acid. After cooling, the ortho-isomer will crystallize out as hydrochloride salt.
Purpose
1. Used as dye intermediates, solvents, fungicides and reagents. Used as an intermediate for pesticides, synthetic resins, etc. Used to prepare ice dye color base, that is, yellow base GC. It can also be used as the diazo component of azo dyes (such as acid black and acid blue) to produce Permanent Yellow R, Permanent Red FR, Hansa Yellow HR, etc.
2. Methyldichloroaniline is a cross-linking agent used to prepare medicines, pesticides and polyurethane resins. It can also be used in organic synthesis.
3. Used as dye intermediates, solvents, fungicides and reagents. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/124-2.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/toyocat-np-catalyst-tosoh/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Catalyst-PT303-PT303-polyurethane-catalyst-PT303.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fentacat-f9-catalyst-cas15461-78-5-solvay/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1112extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40320extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/addocat-so-niax-d-19-pc-cat-t9/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/category/morpholine/page/2/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/high-quality-cas-26761-42-2-potassium-neodecanoate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dibutyltin-diacetate/