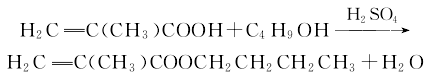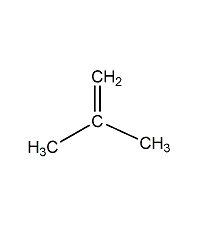
Structural formula
| Business number |
01JK |
| Molecular formula |
C2H2Cl2 |
| Molecular weight |
97 |
| label |
vinylidene chloride,
Vinylidene chloride
|
Numbering system
CAS number:75-35-4
MDL number:MFCD00011653
EINECS number:200-864-0
RTECS number:YZ8061000
BRN number:1733365
PubChem number:24872048
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with unpleasant odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -122.6[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 31.7[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.21[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.3[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 66.5 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1095.9[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 220.8[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.21[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.13 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -19 (CC); -15 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 570[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 16[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 5.6[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.3302
17. Flash point (ºC): 570
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 26.197
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 6.519
20. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, Liquid): 25.1
21. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25.15ºC, constant pressure): 1.155
22. Heat of polymerization (KJ/mol): 60.7
23. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.4249
24. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 16.813
25. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.110×109
26. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 41.430
27. Liquid phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -23.9
28. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1 ·K-1): 112.4
29. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 2.4
30. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 287.98
31. Gas phase standard free energy of formation ( kJ·mol-1): 25.4
32. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):66.93
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[12]
LD50: 200mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 6350ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Asia Acute and chronic toxicity[13]
Animal exposure 0.379g/m3 and 0.199g/ m3, 8 hours a day, 5 days a week, liver and kidney damage will occur after a few months. Exposure below 0.099g/m3 will cause mild liver and kidney disease.
4. Mutagenic[14]
Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 5%��DNA damage: Rat inhalation 10ppm. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: mice were orally administered 200 mg/kg. Cytogenetic analysis: hamster lung 250mg/L.
5. Teratogenicity[15] The lowest toxic dose of inhalation (TCLo) in rats 6~15 days after pregnancy 80ppm (7h), causing developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system.
6. Carcinogenicity[16] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals .
7. Others[17] TCLo: 25ppm (human inhalation)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18]
LC50: 169mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow , static); 74mg/L (96h) (bluegill, static); 220ppm (96h) (red perch, static)
2. Biodegradability None Information
3. Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×10 When 5 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 1.2d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.58
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 79.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 173.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.15
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 27
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Volatile and toxic. It has a tendency to self-polymerize and is easily oxidized by air. After oxidation, chlorine, hydrogen chloride, phosgene, formaldehyde and peroxide are generated. At the same time, this peroxide can promote the polymerization of monomers. It can form copolymers with various ethylene derivatives (such as vinyl chloride, styrene, etc.). Therefore, it is necessary to add a polymerization inhibitor or seal it with an aqueous solution of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and alkali. Copper or brass poses a risk of forming explosive acetylene compounds.
2. It is easily polymerized under the action of light or catalyst, and can be copolymerized with vinyl chloride or acrylonitrile. It easily undergoes an auto-oxidation reaction with oxygen in the air to generate peroxides that are dangerous to explode. Peroxide slowly decomposes to form formaldehyde, phosgene and hydrogen chloride. Generally, a small amount of hydroquinone, phenols, and alkylamines are added as stabilizers. It reacts with chlorine at 40~50℃ to generate 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane. In the presence of anhydrous ferric chloride or aluminum trichloride, it reacts with hydrogen chloride to generate 1,1,1-trichloroethane.
3. Irritating skin and eyes. Inhaling high-concentration vapor can cause central nervous system paralysis and coma. Long-term inhalation of low-concentration vapor can cause damage to the liver and kidneys, and can cause tumors in animals and humans, so please pay attention to ventilation when using it. The inhalation lethal concentration for mice is 25209.5 mg/m3. The olfactory threshold concentration is 1985mg/m3. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 40mg/m3 (USA).
4. Stability[20] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, acids, alkalis
6. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Heating
7. Polymerization hazard[23] Polymerization
8. Decomposition products[24] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored for a long time to avoid deterioration. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Vinyl chloride chlorination method: Vinyl chloride is obtained by chlorination and alkaline hydrolysis. During the chlorination reaction, dichloroethane and s-tetrachloroethane are generated; during the alkaline hydrolysis process, 1,2-dichloroethane is generated. Among them, 1,1,2-trichloroethane is produced by removing hydrogen chloride to produce vinylidene chloride, which is a commonly used method in industry. According to the different alkali used, it can be divided into sodium hydroxide method, calcium hydroxide method and ammonium hydroxide method. The final product of the former has many by-products with a boiling point lower than 30°C and a high content of calcium acetylene chloride, but there is no environmental pollution; the final new technology of the latter has no by-products of calcium chloride and sodium chloride, and post-processing is easy. When using hydroxide, strong stirring is necessary to reduce the possibility of foaming, correspondingly increase the utilization factor of the equipment, and the amount of chloroacetylene generated can also be reduced to 1/10.
①Sodium hydroxide method:This method can be divided into two types. One is that all reactions are carried out in a continuous reactor, the batching ratio (NaOH:CH2ClCHCl2) is (1-1.2:1), and the content of sodium hydroxide is 10%-20%. The reaction temperature is 50-70°C, the product content is 94%, and the yield is 93.9%. The second method is to use sodium chloride-containing sodium hydroxide and 1,1,2-trichloroethane to convert into vinylidene chloride. This method directly uses electrolyte, and the sodium chloride generated after dehydrochlorination can be returned to the electrolysis system for recycling. Therefore, it is most suitable for the production of vinylidene chloride in chlor-alkali plants.
②Calcium hydroxide method: This method can be divided into four types. First, the raw material calcium hydride concentration is 200g/L, the calcium carbonate concentration is <20g/L, the calcium hydroxide excess is 50%, and the system temperature is 80°C at the beginning of the reaction, and then rises to 90-92°C. The crude vinylidene chloride obtained after the reaction is purified by distillation, and the yield can reach more than 80%. Secondly, since the control step of the reaction to generate vinylidene chloride is material transfer at the interface, a small amount of surfactant and water should be added to improve the contact effect. Third, in order to simplify the process, the reaction and distillation are combined in one tower. Fourth, first carry out the addition reaction of vinyl chloride and chlorine through the reactor, and then add 10% calcium hydroxide to convert 1,1,2-trichloroethane into vinylidene chloride. After refining, the product vinylidene chloride is obtained. Ethylene chloride.
③Ammonium hydroxide method: Xudao Company proposed to use ammonium hydroxide to replace sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. The feed ratio is NH4OH:CH2ClCHCl2=2:1 (mol), the reaction temperature is 120℃, and the pressure is about 0.86MPa, conversion rate 52.1%, ammonium chloride, ammonia and unreacted 1,1,2-trichloroethane can be recycled. The chlorination reaction is carried out in a tower reactor. The tower is filled with trichloroethane. Iron rings are stacked in the tower as a catalyst. Chlorine and vinyl chloride are introduced from the bottom of the tower in a ratio of 1.05:1 (mol). The reaction temperature is controlled at 35-45℃. Since the reaction liquid of vinyl chloride and chlorine gas can circulate naturally depending on the temperature difference, it can also be forced to circulate using a pump. The reaction temperature is about 75°C and the pressure is normal pressure. The generated vinylidene chloride passes through the rough separation tower on the kettle and then through the rectification tower to purify and refine the product vinylidene chloride. At present, all domestic factories use kettle-type alkaline hydrolysis reactors, most of which operate intermittently. In the past, some people used 2.5%-3.0% milk of lime as alkali solution, but later switched to dilute sodium hydrochloride solution due to clogging of equipment. In the intermittent operation, the reaction temperature was raised to 85°C in the later stage of alkaline hydrolysis. As a result, the impurities in the crude vinylidene chloride increased significantly, which made refining difficult.
2. Alkaline chlorination method of ethyl chloride: This method uses 1,2-dichloroethane as raw material, and chlorides it into 1,1, 2-Trichloroethane, in addition to 1,2-dichloroethane and chlorine, 12% ethylene is also added to the reactants to accelerate the chlorination reaction of dichloroethane. Trichloroethane is purified in a low-boiling tower and a high-boiling tower and then reacts with a dilute alkali to remove a molecule of hydrogen chloride to obtain vinylidene chloride; crude vinylidene chloride is refined in a low-boiling tower and a high-boiling tower to obtain pure vinylidene chloride. Ethylene Products. The chlorination yield of the above process is 95.4%, the alkaline hydrolysis yield is 99.8%, and the product purity is as high as 99.9%.
3. Methyl chloroform thermal cracking hydrogen chloride method: This method uses vinyl chloride as raw material, and is added with hydrogen chloride to generate 1,1-dichloroethane; dichloroethane is chlorinated at a high temperature of 480°C , the main chlorinated liquid products obtained are vinylidene chloride, methyl chloroform (1,1,1-trichloroethane) and vinyl chloride. By-products include trichlorethylene, cis-dichloroethylene, trans-dichloroethylene, polychlorethane and hydrogen chloride. The chlorinated liquid is distilled to separate the above products, vinyl chloride and hydrogen chloride are returned to the addition process, trichlorethylene is sold as a commodity, methyl chloroform is cracked into vinylidene chloride by high temperature, the cracked mixture and the chlorinated liquid are combined and separated by distillation. Polymerization inhibitor is added to vinylidene chloride for sale as a commodity. 1,1-dichloroethane and 1,2-dichloroethylene are chlorinated in liquid phase at low temperature to form 1,1-dichloroethane and tetrachloroethane, and then sent to Enter the high temperature chlorinator.
4. Ethane chlorination and thermal cracking to remove hydrogen chloride: This method uses ethane as raw material, which is chlorinated at a high temperature of 426.6°C into hydrogen chloride, vinyl chloride, vinylidene chloride, ethyl chloride, A mixture of 1,1-dichloroethane and methyl chloroform is used to separate the above product by fractional distillation. Hydrogen chloride is used in the vinyl chloride hydrochlorination reactor; methyl chloroform is cracked at high temperature to decompose a molecule of hydrogen chloride to generate vinylidene chloride, which is combined with the chlorinated liquid for separation and purification to obtain the high-purity product vinylidene chloride.
5. High-temperature thermal dehydrochlorination method: First, preheat 1,1,2-trichloroethane to 250°C, and then pass it into a tubular reactor for decomposition reaction. The reaction temperature is 350-500°C. The advantage of this method is that the decomposition product hydrogen chloride can be utilized, but the by-product 1,2-dichloroethylene is more.
Purpose
1. This product is a copolymer based on (containing at least 80%), which can produce polyvinylidene with fire resistance. Various synthetic resins can be produced by copolymerizing 1,1-dichloroethylene with acrylonitrile, butadiene, acrylate, styrene, etc. Vinylidene chloride resin can be processed into fibers or films and used for surface coatings on paper or plastic films. Polyvinylidene chloride fiber can be used to produce fabrics, tents, insect nets, car seat cushions, etc. Polyvinylidene chloride film has lower air permeability and moisture permeability than other plastic films, and is suitable for food packaging. Copolymers with methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate, etc. can be used in the film industry. Mainly used as raw material for the manufacture of vinylidene chloride resin and 1,1,1-trichloroethane. Because of its high volatility, it is usually not used as a solvent.
2. Used in the manufacture of various copolymers, synthetic fibers, adhesives and organicsynthesis. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Dibutyltin-monobutyl-maleate-CAS-66010-36-4-BT-53C.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/839extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/pc-cat-nmm-addocat-101-tertiary-amine-catalyst-nmm/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/37-3.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/sponge-foaming-catalyst-smp/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/950extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44867extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44386extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/high-quality-cas-26761-42-2-potassium-neodecanoate/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/tertiary-amine-catalyst-dabco-pt303-catalyst-dabco-pt303/
![]()