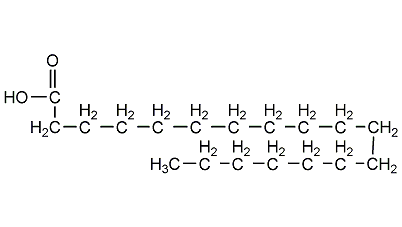
Structural formula
| Business number | 018D |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C18H36O2 |
| Molecular weight | 284.48 |
| label |
stearic acid, n-octadecanoic acid, Carboxylic acid C18, Proviscol wax, n-Octadecanoic acid, accelerator, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:57-11-4
MDL number:MFCD00002752
EINECS number:200-313-4
RTECS number:WI2800000
BRN number:608585
PubChem number:24899616
Physical property data
1. Properties: white waxy transparent solid or yellowish waxy solid. Can be dispersed into powder with slight butter smell.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 0.9408
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 67~69
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 183~184 (133.3pa)
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): 360
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.455
8. Flash point ( ºC):>110
9. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -11446.9
10. Gas phase standard claim Heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -781.2
11. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -11343.4
12. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -884.7
13. Crystal phase Phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -11280.4
14. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -947.7
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water, slightly soluble in cold ethanol, and easier to dissolve when heated. Slightly soluble in acetone and benzene, easily soluble in ether, chloroform, hot ethanol, carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide.
Toxicological data
Intravenous injection of mice and ratsLC50: (23±0.7)mg/kg, (21.5±1.8)mg/kg.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 87.00
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 320.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 770.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 34.49
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for calculation of hydrophobic parameters (XlogP): 7.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 16
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
p>
7. Number of heavy atoms: 20
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 202
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. The pure product is a soft white piece with gloss.
2. Slightly soluble in cold water, soluble in alcohol and acetone, easily soluble in benzene, chloroform, ether, carbon tetrachloride, Carbon disulfide, amyl acetate and toluene, etc. Non-toxic.
3. Exists in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, oriental tobacco leaves and smoke.
4. It is the fatty acid that makes up stearin.
Storage method
1.200 type stearic acid is packed in cardboard boxes. Type 800 stearic acid is packed in woven bags lined with plastic bags. Store in a cool and ventilated place.
2. This product can be packed in cardboard boxes or woven bags lined with plastic bags. The net weight of each box (bag) is 25kg or 50kg.
3. Store in a cool, dry, ventilated place, and be careful to keep away from fire sources and oxidants. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
1. Stearic acid is a fatty acid widely found in nature. Almost all oils contain stearic acid in varying amounts. , the content in animal fat is relatively high, such as butter, the content can reach 24% , the content of vegetable oil is less, and tea oil is 0.8%, palm oil is6%, but the content in cocoa butter is as high34%. There are two main production methods for industrial stearic acid: fractionation method and pressing method. A decomposing agent is added to the hardened oil, and then hydrolyzed to obtain crude fatty acids, which are then washed, distilled, and decolorized to obtain the finished product. At the same time, glycerol is produced as a by-product.
(1) Fractional distillation method Add 6t of cottonseed oil hardened oil to the hydrolysis pot , hydrolyzing agent stearicresolsulfonic acid and stearic naphthalenesulfonic acid 120kg. After steam is introduced until the oil layer is transparent, add 4200kg of water. Continue to heat to boiling, react under normal pressure for 7.5 hours, clarify for 0.5 hours, and separate the lower layer of glycerol water. After that, add 120kg of hydrolyzing agent, add steam and heat until the oil layer is transparent, add 3600kg of water, and react for about 10 hours. The end point of hydrolysis is when the mixed acid value reaches above 190mgKOH/g. After that, it was clarified for 0.5h, and after separating the glycerol water, 7g of salt and 3600kg of water were added for washing. Then use 14kg of salt and 4200kg of water for secondary water washing. After the first step of washing, it was clarified for 0.5h, and after the second step of washing, it was clarified for 2h. After the lower layer of acidic water is separated, take the upper layer of mixed fatty acids and set aside.  Add 2000kg of mixed fatty acids into the distillation kettle and proceed Fractional distillation under reduced pressure, the kettle temperature is 250-255°C, the tower temperature is 210-220°C, the top temperature is 200-210°C, and the residual pressure at the top of the tower is 0.53-0.93kpa. After the feeding, discharging and discharging reaches a balance, it switches to continuous operation, with 100% feeding, 40% discharging and 60% discharging. The raw materials are used to make tertiary stearic acid. After the iodine value of the discharging material is analyzed to be below 2mgl/100g, 1000kg stearic acid and 3kg 92.5% sulfuric acid are put into the pickling pot in sequence, and boiled for washing. After cutting off the acid feet, put 450kg of stearic acid into a decolorizing pot and heat it to 190°C. Add 150ml of chemical soda ash and 11kg of dry clay, and then decolorize at about 105°C under reduced pressure and stirring for about 45 minutes. After filtering and pouring molding�That is, first-level stearic acid is obtained. The glycerin water separated during the hydrolysis process is neutralized with milk of lime at 80-100℃ , refined glycerol can be obtained through processes such as suction filtration concentration, pressure filtration, vacuum distillation, activated carbon decolorization and filtration pressure. (2) Pressing method uses animal and vegetable oils as raw materials, in a hydrolyzing agent (such as zinc oxide) First-grade stearic acid can be obtained through high-pressure hydrolysis, washing, vacuum distillation, pressing, bleaching and crystallization in the presence of alcohol.
Add 2000kg of mixed fatty acids into the distillation kettle and proceed Fractional distillation under reduced pressure, the kettle temperature is 250-255°C, the tower temperature is 210-220°C, the top temperature is 200-210°C, and the residual pressure at the top of the tower is 0.53-0.93kpa. After the feeding, discharging and discharging reaches a balance, it switches to continuous operation, with 100% feeding, 40% discharging and 60% discharging. The raw materials are used to make tertiary stearic acid. After the iodine value of the discharging material is analyzed to be below 2mgl/100g, 1000kg stearic acid and 3kg 92.5% sulfuric acid are put into the pickling pot in sequence, and boiled for washing. After cutting off the acid feet, put 450kg of stearic acid into a decolorizing pot and heat it to 190°C. Add 150ml of chemical soda ash and 11kg of dry clay, and then decolorize at about 105°C under reduced pressure and stirring for about 45 minutes. After filtering and pouring molding�That is, first-level stearic acid is obtained. The glycerin water separated during the hydrolysis process is neutralized with milk of lime at 80-100℃ , refined glycerol can be obtained through processes such as suction filtration concentration, pressure filtration, vacuum distillation, activated carbon decolorization and filtration pressure. (2) Pressing method uses animal and vegetable oils as raw materials, in a hydrolyzing agent (such as zinc oxide) First-grade stearic acid can be obtained through high-pressure hydrolysis, washing, vacuum distillation, pressing, bleaching and crystallization in the presence of alcohol. ![]() (3)In the presence of decomposing agents (sulfonated mixtures such as benzene and naphthalene), the hardened oil, tallow or mutton fat is hydrolyzed, and then acidified, distilled, pressed, and pickled to obtain the finished product.
(3)In the presence of decomposing agents (sulfonated mixtures such as benzene and naphthalene), the hardened oil, tallow or mutton fat is hydrolyzed, and then acidified, distilled, pressed, and pickled to obtain the finished product.
(4). Using oleic acid hydrogenation method.
(5). It is produced by using the C10~C20 and C18~C20 fractions of synthetic fatty acids as raw materials, melting, pickling (using 1% sulfuric acid) casting, pressing, melting, pickling, and dehydration and crystallization. 2. Tobacco: OR, 44; FC, 9, 15, 18, 41, 43, 50; OR, 26; BU, OR, 18; BU, 9; OR, 19.
Purpose
1.200 stearic acid can be used as the activator of vulcanization accelerator for high-grade rubber products, the main raw material of polyvinyl chloride soap stabilizer, the main raw material of cosmetic cream and cold cream, the raw material of high melting point grease and waterproofing agent, and polishing paste. It is the main raw material for lubricating polishing agents and release lubricants for textiles, printing and dyeing, leather and wax paper, and raw materials for cultural supplies such as copy paper, pencils and crayons.
Type 800 stearic acid can be used as a vulcanization accelerator and activator for general rubber products, the main raw material of polishing paste, the main raw material of soap-based grease, and the raw material of stationery. 2.Stearic acid is a fatty acid widely present in nature. Almost all oils contain stearic acid in varying amounts. In addition to being used as an emulsifier for oil-based drilling fluids, it is also used as a vulcanization activator for natural rubber, synthetic rubber (except butyl rubber) and latex, and as a raw material for plastic plasticizers and stabilizers. It is used in medicine to prepare ointments, suppositories, etc., and is also used to make cosmetics, candles, waterproofing agents, polishes, etc. This product is used in the food industry as a lubricant, defoaming agent and raw material for food additives such as glyceryl stearate, sorbitan stearate and sucrose ester. 3.Used as a solvent for determining molecular weight. Preparation of stearates and esters, carbon black diffusing agents, active agents to promote acidification. 4.Used as an emulsifier for oil-based drilling fluids. It can also be used as lubricant and wetting agent in rubber industry and textile industry. 5.Widely used as base raw material for cosmetics such as cream, cold cream, hair cream, lotion, shampoo, etc.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-ne1070-polyurethane-gel-type-catalyst-dabco-low-odor-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-753-73-1/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/polycat-520-catalyst-cas10294-43-5-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1859extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/cas2212-32-0/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dimethyltin-dichloride-cas-753-73-1/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/52.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/amine-catalyst-a-300/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/polyurethane-catalyst-1028/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/103-83-3/