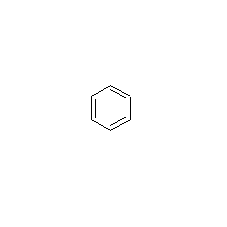
Structural formula
| Business number |
01GH |
| Molecular formula |
C6H6 |
| Molecular weight |
78.11 |
| label |
Benzol,
Cyclohexatriene,
Dehydrating solvent for organic synthesis,
thinner,
paint stripper,
Aromatic hydrocarbons
|
Numbering system
CAS number:71-43-2
MDL number:MFCD00003009
EINECS number:200-753-7
RTECS number:CY1400000
BRN number:969212
PubChem number:24856389
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with strong aromatic smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 5.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 80.1 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.88[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 2.77[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 9.95 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3264.4[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 289.5[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.92[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.15[ 10]
11. Flash point (℃): -11[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 560 [12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.0[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%) : 1.2[14]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone and so on. [15]
16. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.49794
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.6010
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 33.9
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 9.872
20. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC) , gas): 82.966
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 49.051
22. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC, gas): 3303.08
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 1.05
24. Boiling point elevation constant: 2.53
25. Electrical conductance Rate (S/m): 76×10-9
26. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 25ºC): 0.1442
27. Vapor pressure (kPa, 79.5ºC): 41.3
28. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00121
29. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.305
30. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 256
31. Critical compression factor: 0.268
32. Eccentricity factor: 0.211
33. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 5.3823
34.Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 426.70
35. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.706
36.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.000×109
37.van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 48.400
38. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3301.47
39. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 82.89
40. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 269.30
41. Gas phase standard generation Free energy (kJ·mol-1): 129.8
42. Gas phase�Quasi hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 82.43
43. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -3267.58
44. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 48.99
45. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 173.45
46. Liquid phase standard Free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 124.33
47. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):136.06
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 1800mg/kg (rat oral); 4700mg/kg (mouse Oral); 8272mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 31900mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 7h)
2. Irritation[17]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), moderately irritating.
Rabbit eye: 2mg (24h), severe irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18]
Rabbit inhalation 10mg/m3, days to weeks, causing leukopenia and a relative increase in the percentage of lymphocytes. The hematopoietic system of chronically poisoned animals changes, and in severe cases, the bone marrow regenerates poorly.
4. Mutagenicity [19]
DNA inhibition: human leukocytes 2200 μmol/L. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 200 μmol/L. Cytogenetic analysis: Human inhalation 125 ppm (1a). Somatic mutation: human lymphocyte 1gm/L.
5. Teratogenicity[20]
The lowest toxic dose of inhalation (TCLo) in mice 6~15 days after pregnancy 5ppm, causing developmental abnormalities of the hematological and lymphatic systems (including spleen and bone marrow). The lowest toxic dose (TDLo) of 219mg/kg was given to mice intraperitoneally, causing malformations in the development of the hematological and lymphatic systems and the hepatobiliary system.
6. Carcinogenicity [21] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G1, confirmed human carcinogen.
7. Others[22] The lowest toxic concentration (TCLo) for inhalation in rats: 15ppm/24h (gestation 7~14d), causing implantation Increased mortality and abnormal musculoskeletal development.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[23]
LC50: 45mg/L (24h) (goldfish); 20mg/L (24~48h) ) (Bluegill sunfish); 27mg/L (96h) (Shrimp microphylla);
LC100: 12.8mmol/L (24h) (Tetrahymena pyriformis);
LD100: 34mg/L (24h) (bluegill sunfish);
TLm: 36mg/L (24~96h) (rainbow killifish, soft water)
2. Biodegradability [24]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 120~384
Anaerobic biodegradation (h) ): 2688~17280
3 Non-biodegradability[25]
Aqueous phase photolysis half-life (h): 2808~16152
Photolysis maximum light absorption wavelength range (nm): 239~268
Photooxidation half-life in water (h): 50.1~501
4. Bioconcentration [26] BCF: 3.5 (Japanese eel); 4.4 (Atlantic herring); 4.3 (goldfish)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.25
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 89.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 207.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.40
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 15.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Benzene is one of the most important basic organic raw materials and a representative of aromatic hydrocarbons. It has a relatively stable six-membered ring structure.
2. The main chemical reactions include addition, substitution and ring-opening reactions. Under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid and nitric acid, substitution reaction easily occurs to generate nitrobenzene. It reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid to form benzenesulfonic acid. Using metal halides such as ferric chloride as a catalyst, a halogenation reaction occurs at a lower temperature to generate halobenzene. Using aluminum trichloride as a catalyst, it undergoes alkylation reaction with olefins and halogenated hydrocarbons to generate alkylbenzene; it undergoes acylation reaction with acid anhydride and acid chloride to generate acylbenzene. In the presence of a vanadium oxide catalyst, benzene is oxidized with oxygen or air to generate maleic anhydride. Benzene cracks when heated to 700°C, producing carbon, hydrogen and a small amount of methane and ethylene. Platinum and nickel are used as catalysts to perform hydrogenation reaction to generate cyclohexane. Zinc chloride is used as a catalyst to react with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form benzyl chloride. However, the benzene ring is relatively stable and does not react with oxidants such as nitric acid, potassium permanganate, and dichromate.
3. It has high refraction and strong aroma, is flammable and toxic. Miscible with ethanol, ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide and acetic acid, slightly soluble in water.It is non-corrosive to metals, but the sulfur-containing impurities in lower-grade benzene have obvious corrosive effects on copper and certain metals. Liquid benzene has a degreasing effect and can be absorbed by the skin and cause poisoning, so contact with the skin should be avoided.
4. Vapor and air form an explosive mixture, with an explosion limit of 1.5%-8.0% (volume).
5. Stability[27] Stable
6. Incompatible substances[28] Strong oxidants, acids, halogens, etc.
7. Polymerization hazards[29] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[30] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
(1) According to its source and production method, it is divided into petroleum benzene and coked benzene. Petroleum benzene is obtained by hydrogenation, catalytic reforming and separation of light petroleum fractions; coked benzene is crude benzene recovered from coking by-products through washing and fractionation. income. The main difference between the two is that coked benzene has a greater pungent smell.
Benzene is obtained from coal carbonization, catalytic cracking of petroleum, and catalytic reforming. Therefore, the impurities easily contained are mainly aromatic homologues, thiophenes and saturated hydrocarbons. During refining, add 5% to 10% concentrated sulfuric acid and shake vigorously, let it stand and separate into layers. After removing the acid layer, wash thoroughly with water, add calcium chloride and other dehydrating agents, dry and then distill. Other methods include co-distillation with aluminum trichloride, mercury salt treatment and azeotropic distillation. High-purity benzene is easy to solidify and can be repeatedly crystallized and separated. Finally, it is dried with phosphorus pentoxide or metallic sodium and then distilled.
In addition to adding dehydrating agents such as calcium chloride, anhydrous sodium sulfate, phosphorus pentoxide and metallic sodium, the method of removing a small amount of water in benzene can also use a binary azeotrope mixture composed of benzene and water for azeotropy. Distillation. By removing the initial distillation part, it is easy to achieve the purpose of dehydration. Benzene can be recovered by distillation or recrystallization.
Process flow:
(1). Coking by-product recovery benzene coking gas contains 30-60g/m3 of crude benzene (the main components are benzene, toluene, xylene, trimethylbenzene and unsaturated compounds , sulfide, etc.), the method of recovering crude benzene is to use washing oil (230-300°C fraction of tar or 260-350°C fraction of petroleum) to absorb in a benzene washing tower at 15-20°C. Generally, benzene washing is often connected in series. In towers 2 to 3, the wash oil is called rich oil after absorbing crude benzene, and contains about 2% to 4% of crude benzene. The rich oil passes through the condenser and is heated to about 80°C with the crude benzene and washed oil vapor coming out of the top of the benzene removal tower. Then it passes through the heat exchanger and heat-exchanges with the hot lean oil flowing out of the bottom of the benzene removal tower, and the rich oil is further heated to 100℃, and then heated to about 160℃ in a tubular heating furnace. Part of the crude benzene and washing oil have been vaporized, and the rich oil composed of a mixture of liquid phase and gas phase enters the debenzene tower and the direct steam introduced at the bottom of the tower and the The oil and gas from the regenerator undergoes steam distillation. The lean oil of crude benzene is steamed out and discharged from the bottom of the tower. It flows to the heat exchanger and is cooled from 135 to 150°C to 110 to 105°C. Then it is added to the hot lean oil tank, further cooled to 25 to 30°C, and then sent back to the benzene washing tower for circulation. use.
The steam discharged from the top of the benzene removal tower, with a temperature of 125~140°C, enters the lower part of the fractionator, is cooled to 90~95°C, and then escapes from the top of the fractionator and enters the middle of the two benzene towers. There are indirect steam heating pipes and direct steam pipes at the bottom of the tower. Light benzene is evaporated from the top of the tower, and the heavy benzene liquid is led from the bottom of the tower to the heavy benzene cooler, where it is cooled to 40-45°C with water and enters the heavy benzene storage tank. The light benzene vapor coming out of the top of the benzene tower has a temperature of 70-75°C and enters the condensation cooler. The condensate cooled to below 30°C enters the separation cylinder. After the water is separated, part of it is refluxed and part of it is sent to the storage tank. Then it is sent to the initial distillation tower. The fraction before 90°C is the initial fraction. After the fraction between 90 and 150°C is condensed by the cooling condenser, it is added to the scrubber with stirring for pickling. The amount of sulfuric acid accounts for about 5% to wash away the unsaturated hydrocarbons. and sulfide and other impurities, then add water to wash. Then add 20% caustic soda solution for neutralization, and finally send it to the distillation tower for distillation. The benzene fraction can be obtained at 79.5~80.6℃; the toluene fraction can be obtained at 110~111℃; the xylene fraction can be obtained at 135~145℃; the solvent oil fraction can be obtained at around 150℃; the residual oil is black Coumaron. Pure benzene, power benzene and pure toluene can be obtained by further distillation of the benzene fraction.
(2) Catalytic reforming method The catalysts used in catalytic reforming mainly include platinum-based (Pt, Pd, Re, etc.) catalysts, and non-platinum-based catalysts (MoO3, Cr2O3, etc.) are also used. Due to different catalysts, the reactor types and catalyst regeneration methods are also different, and the reaction conditions are also different. Among them, the fixed-bed non-regenerative platinum reforming is the most representative. The catalyst in this process is platinum (0.3% ~ 0.6%) supported on alumina and silica. This way the catalyst has a longer life and can generally work for 6 months. No need to regenerate for more than 1 year. The boiling point range of the feed oil depends on the target product. If aromatic hydrocarbons need to be produced, straight-run gasoline of 60 to 130°C should be used. If benzene is mainly produced, narrow-cut straight-run gasoline of 60 to 85°C should be used. The reaction pressure is 3.5~5.2MPa, and the reaction temperature is 490~510℃. The process is as follows: first separate the light components of the raw oil in the pre-separation tower, and then draw out the heavy components.��The raw materials are mixed with circulating hydrogen and then enter the heating furnace. The heated mixed gas enters the fixed-bed catalytic reactor installed in series. After the reaction product is cooled by heat exchange, it enters the high-pressure gas-liquid separator. The gas product passes through the circulating compressor After compression, it is recycled. The liquid is extracted with diethylene glycol ether, an industrial solvent, to separate aromatic hydrocarbons from non-aromatic hydrocarbons, and then sent to the distillation tower to collect the 79.7-80.5°C fraction, which is pure benzene.
(3). Pyrolysis gasoline to benzene produced by pyrolysis gasoline generally contains 40% to 70% aromatic hydrocarbons. Aromatic hydrocarbons contain about 37% benzene, about 14% toluene, and about 5% xylene. Benzene is extracted by hydrodealkylation. First, pyrolysis gasoline is subjected to two-stage catalytic hydrogenation, catalytic dealkylation and hydrogen purification to convert alkylbenzene into benzene, and then benzene is obtained through fractionation.
Continuously wash the industrial benzene with concentrated sulfuric acid to remove the impurity thiophene content, then wash it with water and 5% sodium hydroxide solution, dry it with anhydrous calcium chloride, and distill the supernatant liquid.
(2) According to the sulfide content in industrial benzene, add an appropriate amount of 42% sodium hydroxide solution, 95% ethanol and lead acetate, and mix well. Continue stirring until the sulfide test is qualified (measure the sulfide content every 2.5 hours). Stop stirring and let it stand for 1 hour. After releasing the lower sodium hydroxide solution, wash it with sufficient distilled water 3 to 5 times, stirring for 0.5 hours each time, and let stand. Leave for 0.5h to separate the lower water layer. Then add an appropriate amount of concentrated sulfuric acid under stirring, wash the benzene liquid until the thiophene content is qualified, stir for 2 hours each time, let it stand for 0.5 hours, and then release the lower acid liquid. After pickling, wash twice with water, then add 20% sodium hydroxide solution, stir for 0.5h, let it stand, and separate the alkali layer until it is qualified. Then dry and dehydrate using calcium chloride. The dehydrated benzene is distilled, and the clear distillate is collected as the finished product.
(3) Use coking by-product recovery method, platinum reforming separation method and pyrolysis gasoline extraction method. The coking by-product recovery method uses crude benzene recovered from coking by-products as raw material, which is obtained by initial distillation and then rectification. The platinum reforming separation method is to use the light gasoline obtained by normal pressure distillation to be first catalytically hydrogenated, then reformed with platinum, extracted with diethylene glycol ether, and finally separated by rectification. The pyrolysis gasoline extraction method uses pyrolysis gasoline as raw material, converts alkylbenzene into benzene by hydrodealkylation method, and then obtains it through fractionation.
Purpose
1. Used as an important raw material for synthetic dyes, synthetic rubber, synthetic resin, synthetic fibers, synthetic grains, plastics, medicines, pesticides, photographic films and petrochemical products. This product has good solubility and is therefore widely used Used as adhesives and industrial solvents such as varnish, nitrocellulose paint thinner, paint stripper, lubricating oil, grease, wax, celluloid, resin, artificial leather and other solvents.
2. Standard sample for measuring refractive index. It can be used as a solvent and cleaning agent for precision optical instruments, electronic industry, etc., organic synthesis, etc.
3. Used as analytical reagents, such as solvents and standard materials for chromatographic analysis.
4. Cosmetic solvents. It is mainly used as a diluent for cosmetics such as nail polish to accelerate drying and hardening and improve the solubility of skin film components such as resin.
5. Used as solvents and synthetic benzene derivatives, spices, dyes, plastics, medicines, explosives, rubber, etc. [31]
extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/catalyst-pc41/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-pm-40-low-viscosity-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/butyl-tin-triisooctoate-cas23850-94-4-fascat9102-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/865extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44974extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/38916br>extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/bismuth-metal-carboxylate-catalyst-catalyst-dabco-mb20/extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/bismuth-octoate/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-sa-201-tertiary-amine-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dioctyldichlorotin-95-cas-3542-36-7/