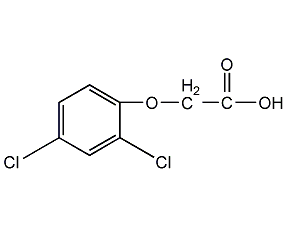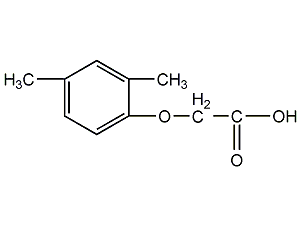
Structural formula
| Business number |
0284 |
| Molecular formula |
C9H9ClO3 |
| Molecular weight |
200 |
| label |
2-Methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid,
2methyl 4 chlorine,
2-Methyl-4-chloro,
Agroxon,
Chwastox,
Emcepan,
herbicide
|
Numbering system
CAS number:94-74-6
MDL number:MFCD00004306
EINECS number:202-360-6
RTECS number:AG1575000
BRN number:2051752
PubChem number:24855166
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and odorless crystals.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 118~119
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, KPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): 2
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg,ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure ( kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Hardly soluble in water, easily soluble in most organic solvents.
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild irritation.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 700mg/kg
Mouse oral LD5O: 550mg/kg
Rabbit transdermal LD5O: 1000mg /kg
Rabbit acute percutaneous LD5O: 2000mg/kg
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 48.77
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 157.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 400.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 19.33
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3.Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecules Polar surface area 46.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 184
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Number of determined atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. The packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
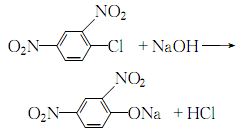
1. Obtained from o-cresol through condensation, acidification and chlorination. Put 26.24kg of o-cresol, 13.9kg of water, and 27.37kg of 35% sodium hydroxide solution into the condensation pot, stir and blend below 70°C to form o-cresol sodium salt. In 21.88kg chloroacetic acid and 41.66kg water, slowly add 26.56kg of 35% sodium hydroxide solution below 25°C to make the pH value 5-6, and acidify at 60°C for 20 minutes. The reactants are heated to 90-95°C in a dephenolization tank and dephenolized by hot steam. Then chlorine at pH 1-2, 60-65°C. After cooling, filtering and washing with water, 2-methyl-4-chlorine is obtained. The original drug, 2-methyl-4-sodium chloride, is dark brown powder. According to HG 2-1460-82, the active ingredient content is ≥56.0%. Raw material consumption quota: o-cresol 730kg/t, liquid chlorine 600kg/t, chloroacetic acid 740kg/t, liquid alkali 3000kg/t, hydrochloric acid (30%) 180kg/t.
2. The production methods of 2-methyl-4-chloride can be summarized as condensation first and then chlorination and first chlorination then condensation. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. The production principle of condensation first and then chlorination is as follows.
Condensation: React at 100~105℃ for 1 hour, and the condensation reaction is completed.
Add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to about 5 for acidification. Carry out dephenolization treatment at 90~95℃.
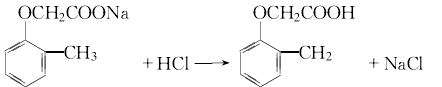
Chlorination and hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value 1 to 2 , pass chlorine at about 60°C for chlorination, and after reaching the end point, cool, filter, and wash with water to obtain 2-methyl-4 chlorine.
Salt formation Since 2-methyl-4 chlorine has low water solubility, it is difficult to directly use it for weeding in farmland. In industry, it is often formulated into sodium salt, ammonium salt or ester.
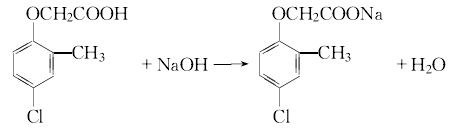
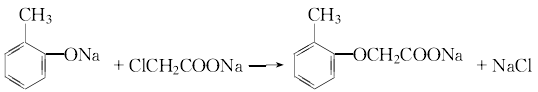
3.Sodium o-cresol is prepared from the reaction of o-cresol, water and liquid alkali. In addition, dissolve chloroacetic acid in water and slowly add liquid caustic soda at room temperature to form a sodium chloroacetate solution. Then slowly add the prepared sodium chloroacetate aqueous solution to the sodium o-cresol solution to perform a condensation reaction. After treatment, add hydrochloric acid for chlorination. After cooling, filtering, and washing with water, 2-methyl-4-chloride is obtained. The product is 2-methyl-4-chloride sodium salt, which is processed into aqueous solution.
Purpose
1. Used as agricultural herbicide.
2.Hormone-type selective herbicide. It can destroy the metabolism of plants, causing them to deform, become swollen, crack, moldy and die. It is suitable for eliminating weeds in grass crops, such as small grains, rice, peas, and lawns, and controlling a variety ofannual and perennial dicotyledonous broad-leaf weeds and some single weeds. For leaf weeds, the dosage is 0.28~2.25kg (active ingredient)/hm2 (1hm2=104m2). It is also effective in killing broadleaf grass and three-edge grass. This product has a great impact on broad-leaf crops such as cotton, soybeans, melons and vegetables, and will die after spraying. Cannot be mixed with acidic pesticides.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1095extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/dabco-tertiary-amine-catalyst-polyurethane-tertiary-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/toyocat-rx3-organic-amine-catalyst-tosoh/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44716extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1023extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/nn-diisopropylethylamine-cas7087-68-5/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dibutyltin-acetate-cas1067-33-0-tributyltin-oxide/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45010extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44424extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-c-225-amine-catalyst-momentive/